Mechanism Of Diet Induced Thermogenesis
Fats have relatively little.
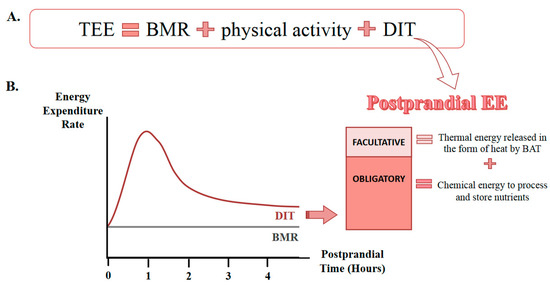
Mechanism of diet induced thermogenesis. The energy required to digest and assimilate the food. Also known as thermic effect of food. An obligatory process of energy expenditure that is strongly related to meal size composition and the physiological characteristics of the individual and a regulatory component that is strongly influenced by the sympathetic nervous system sns table 92 1 a higher dit for a given meal would imply that less. 2 a close correlation was found between brown adipose tissue na k adenosinetriphosphatase na k atpase activity in vitro and in vivo measurements of resting oxygen consumption vo2.
Saito m matsushita m yoneshiro t and okamatsu ogura y 2020 brown adipose tissue diet induced thermogenesis and thermogenic food ingredients. Bile acids brown adipose tissue diet induced thermogenesis food ingredients gut hormone obesity sympathetic nervous system transient receptor potential channels. You re doing great already. Protein plays a key role in body weight regulation through satiety related to diet induced thermogenesis.
It typically represents only about 10 of total daily energy expenditure and is related to the type and amount of food ingested. Diet induced thermogenesis is one of the three components of daily energy expenditure along with basal metabolic rate and activity. Protein induced thermogenesis has an important effect on satiety in conclusion the main determinants of diet induced thermogenesis are the energy content and the protein and alcohol fraction of the diet. The plane of nutrition.
Measured as an increase in body heat production after eating. Thus diet induced thermogenesis as evidenced by the increase in oxygen consumption in rats fed the cafeteria diet was not determined by increased oxygen consumption by bat. You already burn calories naturally when you eat without trying. Measuring conditions include nutritional status of the subject physical activity and duration of the observation.
Here data on diet induced thermogenesis are reviewed in relation to measuring conditions and characteristics of the diet. This conclusion has been corroborated in a study showing that oxygen consumption increases comparably in ucp1 and ucp1 mice when the diet is switched from. 1 the sympathetic noradrenergic activation of brown adipose tissue and the biochemical mechanisms involved in diet induced thermogenesis were studied in rats. Daily energy expenditure consists of three components.
Since the time of lavoisier it has been known that the ingestion of foods by animals and humans produces an increase in oxygen consumption. Still you can optimize the thermic effect of feeding to burn more fat and lose weight. This increase in metabolic rate originally called specific dynamic action sda is now widely referred to as the thermic effect te of food or diet induced thermogenesis dit.