Regulation Of Diet Induced Thermogenesis

As noted above adaptive thermogenesis is reduced during fasting and increased during overfeeding.
Regulation of diet induced thermogenesis. Browning and beiging of adipose tissue. Its role in the regulation of energy homeostasis and as a potential target for alleviating metabolic diseases relation of diet induced thermogenesis to brown adipose tissue activity in healthy men. Research article call for papers. In humans the possible contribution of bat thermogenesis to dit and regulation of energy balance have been suggested by studies on single nucleotide polymorphism in some bat related genes.
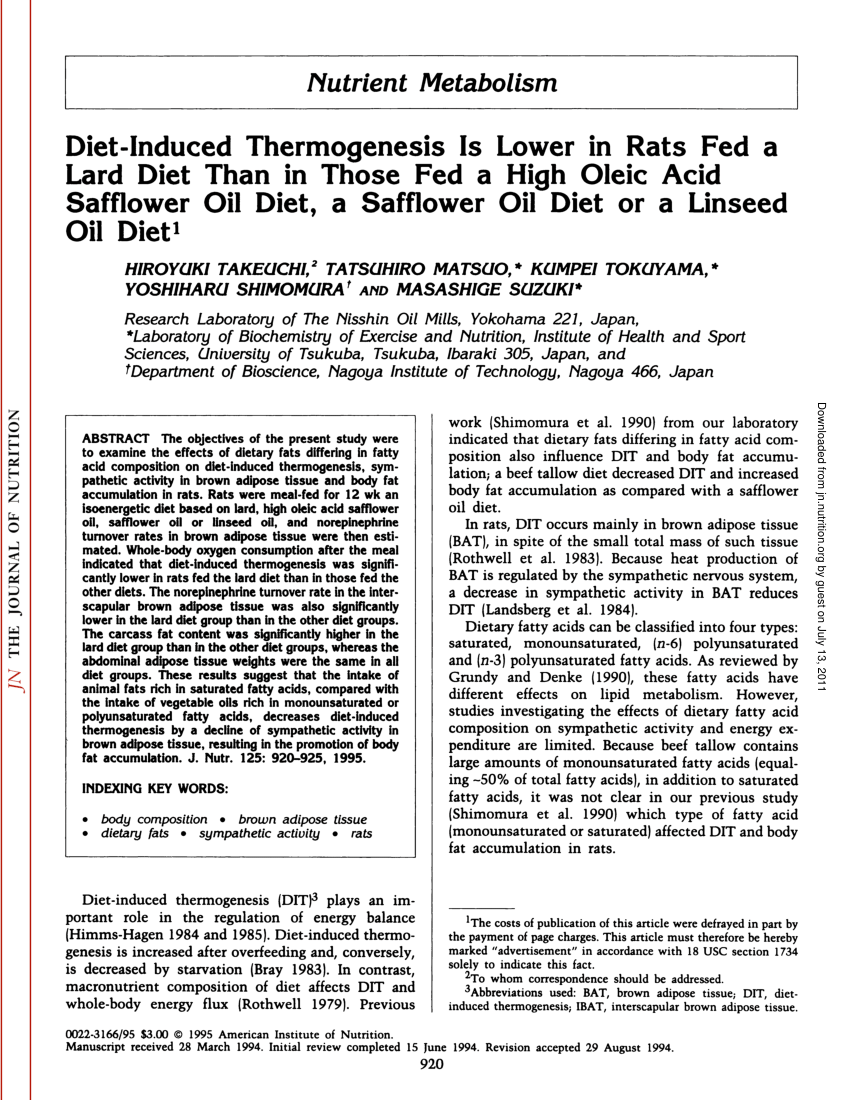
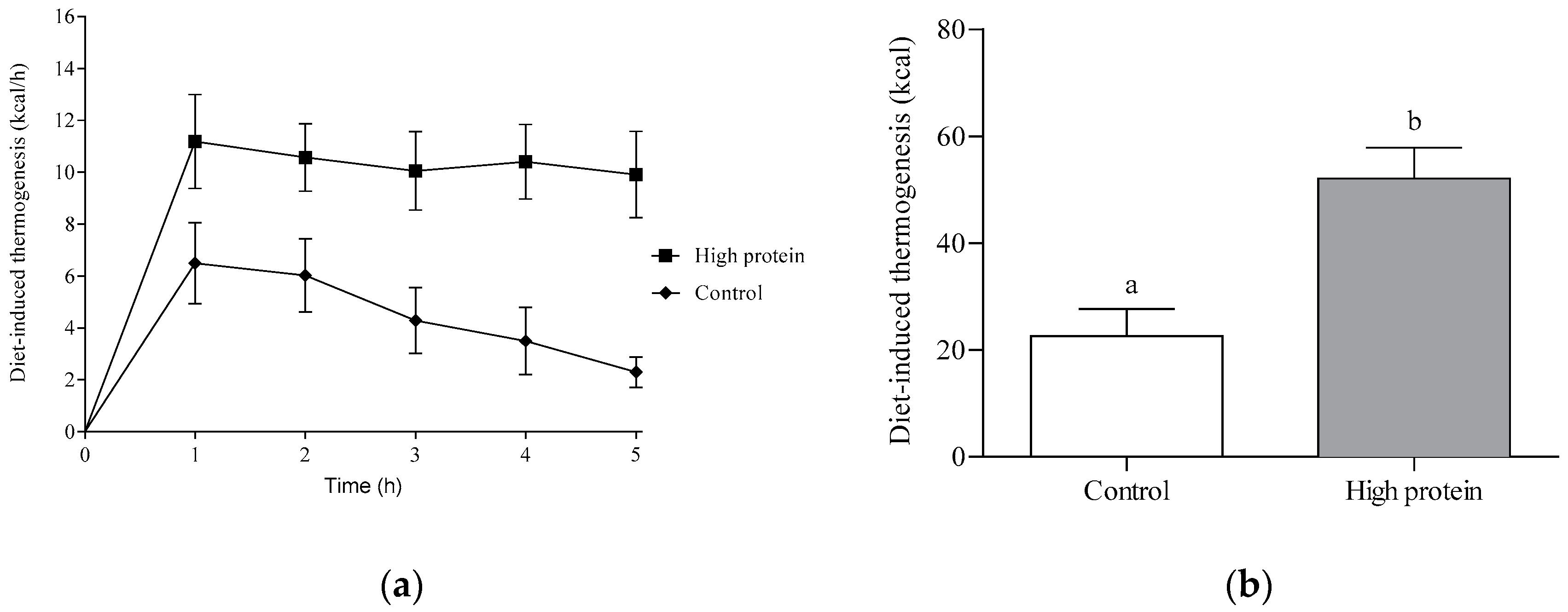
Protein plays a key role in body weight regulation through satiety related to diet induced thermogenesis. Systemic regulation of diet induced thermogenesis in bat. Protein induced thermogenesis has an important effect on satiety in conclusion the main determinants of diet induced thermogenesis are the energy content and the protein and alcohol fraction of the diet. Increased metabolic rate in the overfed state is known as diet induced thermogenesis and is understood to comprise two components.
Diet induced bat thermogenesis in humans. Thermogenesis the metabolic expenditure of energy as heat is the primary way in which mammals loss dietarily derived energy and some evidence suggests that certain obese humans may have defective diet induced thermogenesis.