Adherence To Mediterranean Diet In A Spanish University Population

14 24 years 49 70 men.
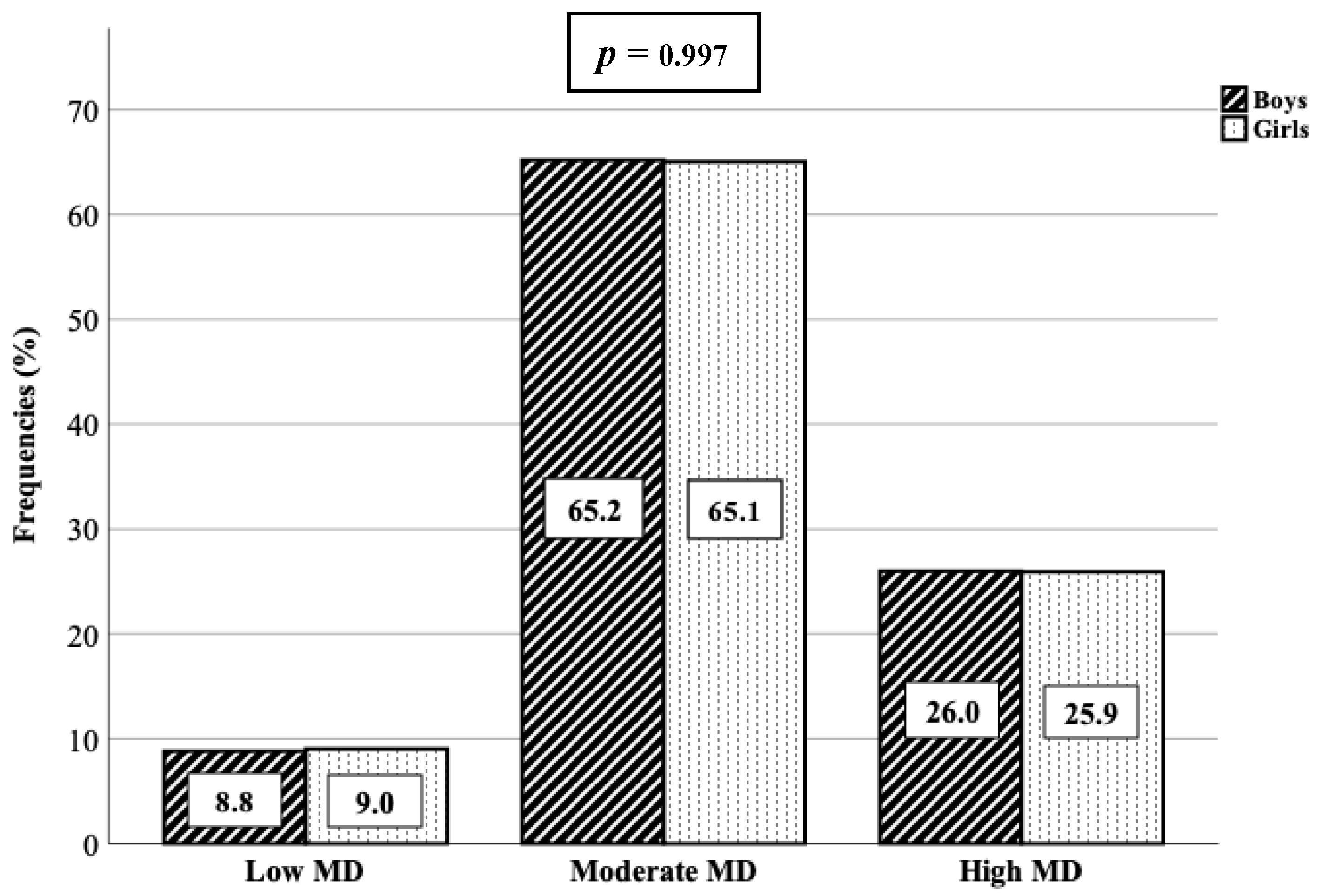
Adherence to mediterranean diet in a spanish university population. The aim of this study is to investigate whether adherence to the mediterranean diet changed during the period 1991 2006 in an italian population. The aim of the present study was to describe mediterranean diet md adherence within a population of adolescents and to analyse the association of multiple factors with adherence. We recruited 501 individuals aged 35 75 without cardiovascular disease by random sampling 55 90 plusmn. The diet of the studied university population showed a low quality with a low intermediate adherence to mediterranean diet due to the fact that more than 80 of subjects need changes forward to a healthier pattern the main deviations were low intake of vegetables and fruit and a high consumption of meat and dairy products.
This included a consideration of diverse physical and mental health indicators. Adherence to mediterranean diet in a spanish university population. The objective of this study is to analyze the influence of adherence to the mediterranean diet mda and its components on early vascular aging eva in a spanish population sample free of cardiovascular disease and to analyze the differences by sex. We derived data from the comparison groups of a.
The consumption of fruits fish legumes nuts and olive oil expressed as g 4 18 mj of energy intake increased significantly with higher adherence to the mediterranean diet in both genders whereas this trend was observed for the consumption of total cereals whole grain cereals and pulses only in men conversely the consumption of meat sweets and pastries in both genders and fast. It is necessary to foster changes toward a healthier diet pattern according to cultural context in this population for. 214 spanish university students predimed sf 36 and gpaq the physically active subjects have a better perception of quality of life related to health and greater md adherence theodoridis et al38 cross sectional descriptive study 987 students 449 males 538 females from the balearic islands university diet diversity score mediterranean diet. The diet quality of 100 nutrition students from amsterdam being considered a non mediterranean population was compared with the diet quality of 85 students from thessaloniki greece.
Article in appetite 78 march 2014 with 182 reads how we measure reads. 51 surprisingly it was found that students at both sites demonstrated an average adherence to the md with slightly higher scores in the dutch sample compared.